

THCA vs. THC: Potency, Effects, Benefits and The Role of Decarboxylation
As we dive deeper into cannabis innovation, novel and minor cannabinoids are offering new potential for target therapeutic use of cannabis. THCA, the not-so-distant cousin of THC, maybe just the thing you’ve been looking for. If you’re looking for the full benefits of cannabis without the headiness or the high - this molecule may be a better choice.
These two compounds, although intimately connected through their biochemical lineage, reveal surprising differences that may reshape how we use cannabis medicinally.
How are these two phytochemicals different; what makes them so similar? In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about THCA vs. THC and how you can utilize both to elevate your cannabis experience.

Understanding the difference between THCA vs. THC

Comparing these two compounds, we can notice something interesting. Their similarities stem from the fact THC is derived from THCA. However, their differences are pretty surprising.
THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is considered an acidic cannabinoid and a precursor to THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). When exposed to heat or UV light, THCA undergoes an enzymatic process known as THCA synthase to yield THC, its popular and psychoactive cousin.
Although the cannabis plant produces many hundreds of cannabinoids, the chemical compounds that are responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis are few in number. This chemical change can occur in the resin glands of the cannabis flower but also occurs when processed and handled with heat after freshly harvested cannabis.
Baking, burning, and vaporizing THCA will convert it to THC instantly. But before we dive too deep into the chemistry of these curious cannabinoids, let’s break down their key differences and similarities.
Above all, THCA and THC differ in their effects on the body. Though there are some cross-over benefits, THCA will never induce paranoia and other symptoms related to potent THC. It is relatively subtle and won’t get you high, making it an exciting alternative for therapeutic use.
The potency of THCA and THC

Though both compounds produce psychoactive effects, THC is typically categorized as a more potent option with intensified effects at higher doses. THCA has the potential to make THC even stronger when decarbed. However, THCA does not produce the intoxicating effects that THC does.
It can increase the actual amount of THC consumed and should be considered when selecting your dose size. Examining product labeling and test results is a great way to keep yourself informed as to how much THC and THCA are present in your flower or concentrate – so you can dose easily and know what you’re smoking!
Therapeutic uses
On their own, both THC and THCA show a lot of potential for medicinal applications. It’s important to note that though these two cannabinoids have unique benefits, they are even more beneficial when paired.
The entourage effect with cannabis is the theory of how all of the compounds found in cannabis resin have synergistic effects, working together to provide enhanced medicinal and pain-relieving effects.
In cases where these cannabinoids were isolated, researchers have begun examining different uses and have found:
Potential health benefits of THCA
Anti-inflammatory psychoactive properties
Improve and regulate appetite
Reduce nausea
Pain relief
Improved sleep
Mental clarity
Non-psychoactive effects
Potential health benefits of THC
Euphoric and relaxing state-altering effects
Reduce physical and mental stress
Pain management
Reducing nausea associated with chemotherapy
Reduction in muscle spasms and cramping
Uses of THCA and THC
Consuming THC can be pretty simple and versatile, depending on your personal preference. It can be easily smoked, vaped, or cooked into your favorite edibles. Getting THCA into your system is a little bit more complicated.
To consume THCA without converting it into THC, you must avoid processes that heat your cannabis. Smoking and baking are not options if you want to ensure you are getting a proper dose of THCA.
If you’re looking to enjoy the benefits of THCA, use raw cannabis plants or oils that have been pressed and extracted without any exposure to heat or light. This can be added to tinctures, capsules, or even a delicious and hearty smoothie.
Legal difference

Lastly, the regulatory distinctions between THCA and THC play a huge role in the research and retail access to these compounds. THCA remains in an ambiguous legal status in the US and is not classified as a federally banned substance. Despite this gray area, THCA is still an analog of THC, and thus it is possible for THCA to be considered illegal based on the Federal Analogue Act. This act was established to outlaw substances that can convert into other scheduled compounds.
At the state level, both THCA and THC are considered legal in many US states, but it is always best to check local and state guidelines on cannabis laws.
Decarboxylation makes all the difference

Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that occurs that removes a carboxyl group from a molecule, releasing CO2 (carbon dioxide). This process occurs when hemp and cannabis plants and fruits are exposed to elemental changes like heat, light, and oxygen and play a key role in fermentation and ripening.
Though cannabinoids can begin decarbing within the live plant, most of the decarboxylation happens in the post-harvest processing and extraction of the oils. This is how we get all the unique cannabinoids and terpenes in a perfectly cured bud.
We can further decarb cannabis flowers and extracts by heating or burning them prior to consuming them.
When considering whether to decarb THCA or not, this depends on how high of a concentration of THC you wish to consume. THCA very effectively and immediately converts into pure THC when exposed to flame, creating a potent and psycho-active experience. This can be very enjoyable for some consumers, but must be handled with care as a heavy dose may induce fatigue, dizziness, or paranoia.
Choosing not to decarb your THCA is also a valid option. You won’t run the risk of having an altered state of mind or any of the side effects associated with cannabis, but you may just get all the benefits of THC without the high! To better understand the difference, we must first understand how these different cannabinoids affect the body.
The difference between the effects of cannabinoids and cannabinoid acids?
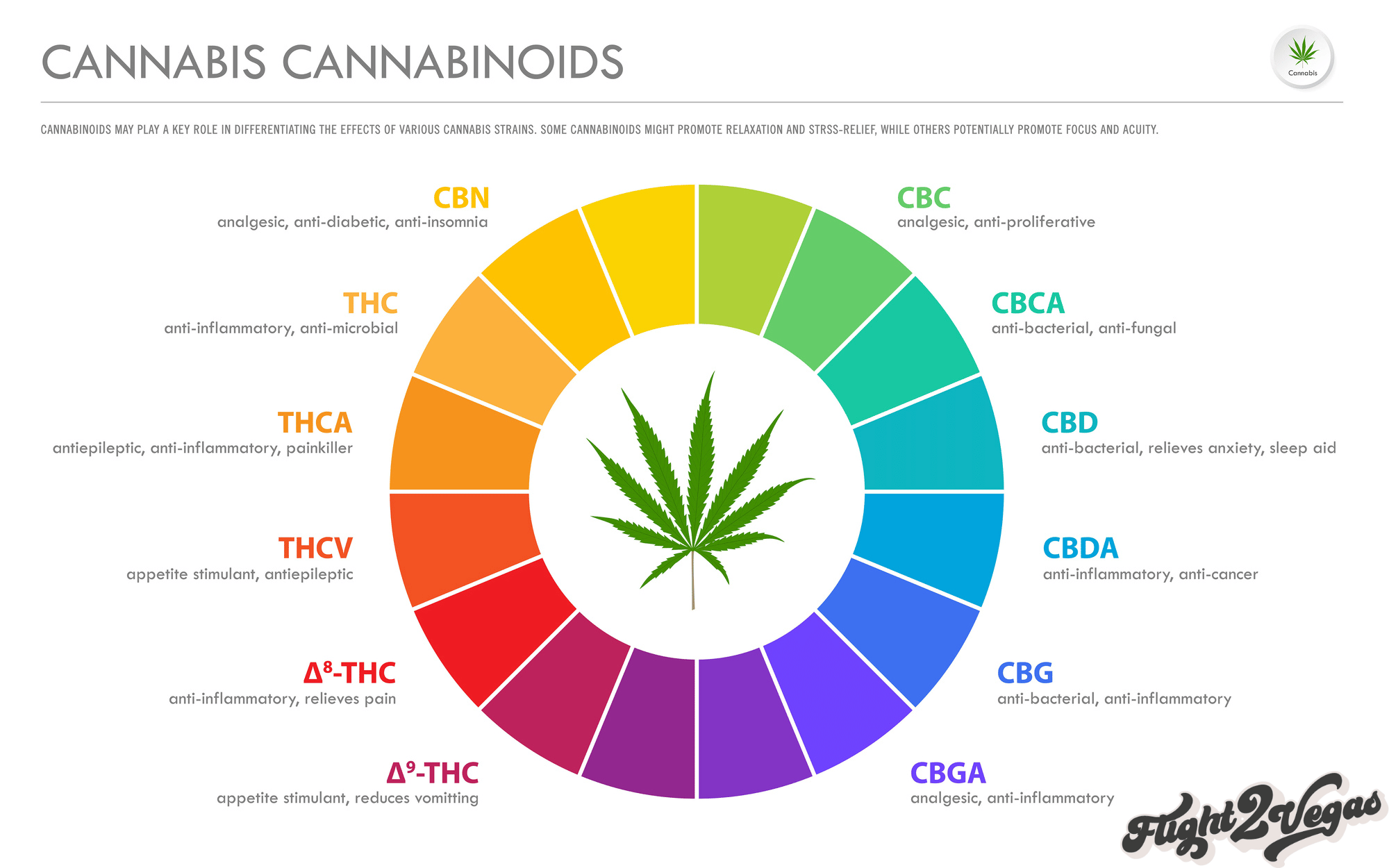
In order to produce cannabinoids like CBD and THC, first come the cannabinoid acids. These precursor compounds undergo enzymatic processes that shift and change their structure, converting them into the many major and minor cannabinoids we know and love.
Both of these categories of phytochemicals are metabolized and processed in the ECS (endocannabinoid system) within the nervous system. While THC and some other cannabinoids directly target and interact with cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, cannabinoid acids act a little differently.
These compounds do not bind in the same way in the nervous system, and work in a more peripheral way. This offers a more subtle sensation along with neuroprotective properties that could be monumental in preventive care for neurodegenerative disease.
There is still so much more to understand, and research on the therapeutic effects of cannabinoid acids is sparse. However, there is still so much optimism as we uncover many more novel cannabinoids and explore their effects on health and well-being.
Additional cannabinoid acids present in flowers and extracts:
CBGA (Cannabigerolic acid)
CBDA (Cannabidiolic acid)
CBCA (Cannabichromenic acid)
CBGVA (Cannabigerovarinic acid)
THCVA (Tetrahydrocanabivarinic acid)
CBDVA (Cannabidivarinic acid)
CBCVA (Cannabichromevarinic acid)
What is Hash and does it contain THC?
Beyond fresh flower or tincture formulas, hash is a classic way to try THCA or THC. In its raw cannabis extract form, hash, also known as hashish, is a high THCA resin extract, rich with many other phytochemicals from cannabis. Hash typically does not contain much THC unless the cannabis plant material used to make it was older or exposed to heat, light, and oxygen. In order to convert hash into THC, it must be smoked or dabbed.
This versatile option is a great way to experiment with THC and THCA to see what combination of the two makes you feel the best. Just be careful eating it straight up, as the chlorophyll and other aromatic compounds may come with a bitter and earthy flavor.
Finding your perfect cannabinoid profile should be fun, and compounds like THCA can ensure a mild but pleasant experience with cannabis. Try incorporating this awesome cannabinoid into your routine for some relief and deep restoration of your mind and body.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is THCA as potent as THC?
No, THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is not as potent as THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol). THCA is a non-psychoactive precursor to THC found in the raw cannabis plant. It only becomes psychoactive THC through decarboxylation, typically by applying heat.
Can THCA cause a high?
No, THCA itself does not cause a high. Heat must be applied to THC-A for that carboxylic acid group to break off and allow the compound to convert into psychoactive THC.
What is THCA and what does it do?
THCA, or Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in raw and live cannabis. As the precursor to THC, THCA converts to THC when exposed to heat through a process called decarboxylation. THCA is believed to have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, making it potentially beneficial as a medical cannabis plant.
What type of smoking is hash?
Hashish or concentrate is typically smoked in a pipe or stream pipe. This can be rolled in a bottle or smoked with a vaporizer of marijuana if desired.











Leave a comment